
Strip Foundation Types of the Soils, Design, Cost Architecture, Soil, Design
Strip foundations (or strip footings) are a type of shallow foundation that are used to provide a continuous, level (or sometimes stepped) strip of support for linear structures such as walls or closely-spaced rows of columns that are built on top of the foundation, placed centrally along their length. When are strip foundations suitable?

Image result for drawing detail drilled concrete pier patent Building foundation, Structural
Refer to the Foundation Systems diagram above. All footings are considered foundations, but not all foundations are footings. Difference between Deep and Shallow Foundations.. Wall footings, also known as strip footings, support the weight from load-bearing and non-structural walls. Similar to isolated footings, the greater the footing area.
Strip Foundation Construction and Design DIY Doctor
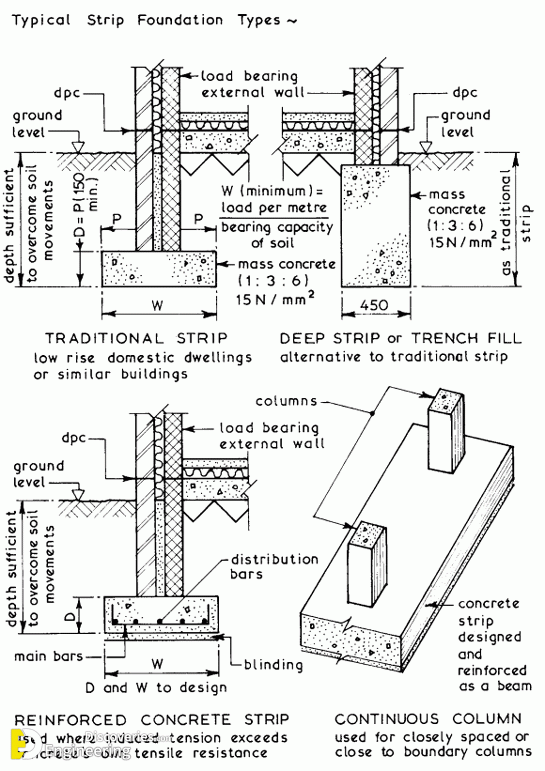
Strip foundations. 2 x S, or; T (maximum 500mm), or; 300mm, whichever is largest. Trench fill foundations. 2 x S, or; one metre, whichever is largest. 4.3.9 Excavations. Excavations for strip and trench fill foundations shall: a) take account of the design dimensions b) take account of localised effects c) be compact, reasonably dry, even and.

What is deep strip foundation Strip foundation Designing Buildings Build and More
A strip foundation is a type of shallow foundation that consists of a long and narrow footing that supports a load-bearing wall. It is typically used for small to medium-sized structures that have relatively low loads.
What Is Strip Footing? Engineering Discoveries
Looking for Steel Reinforcement? We stock everything you need for the reinforcement of your strip foundation; from loose cut and bent rebar to prefabricated cages, mesh, and all the accessories you'll need to do the job right. LEARN MORE GET IN TOUCH The Benefits of Strip Foundations

Spread Footings and the Details Before Construction Engineering Feed
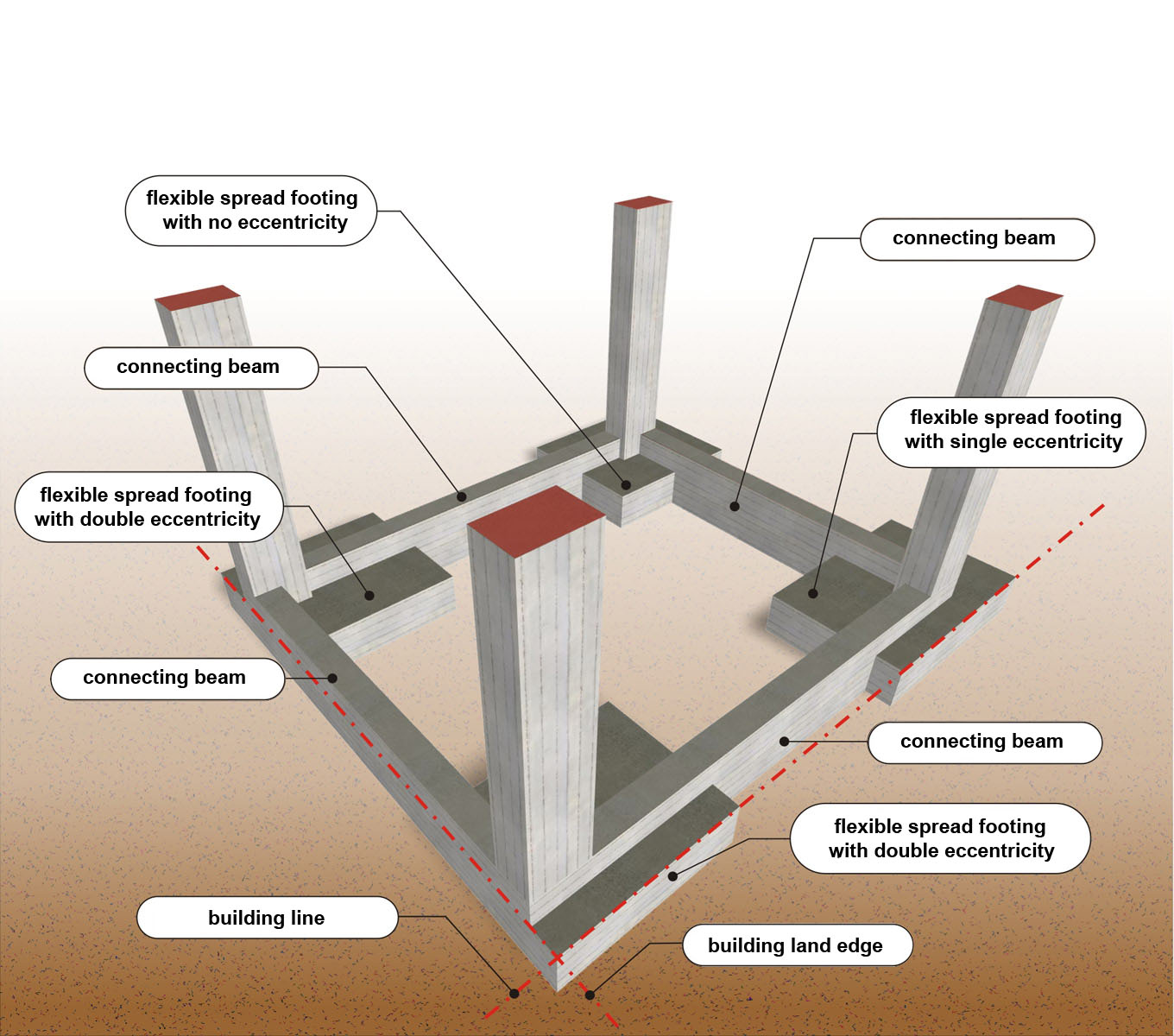
Strip foundation Continuous beam Seismic loading model The effect of tortional stiffness Modeling floor diaphragms 1st example 2nd example 3rd example Unfavourable-loadings Analysis-using-tables Cantilevers, one way slabs Two-way slabs One-storey plane frames Coupled one-storey plane frames Multistorey plane frames

A wall footing or strip footing is a continuous strip of concrete that serves to spread the
As the name suggests, strip foundations form a continuous strip that supports a linear structure, such as a load-bearing wall or closely-spaced rows of columns. Constructed from concrete, strip foundations are placed beneath the wall or column alignments, essentially acting as a continuous base on which these structural elements rest.
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B Concrete Construction
A strip foundation contains much less concrete. A Strip footing is more labour intensive and it needs shuttering to form the shape of the footing. How To Build A Strip Foundation. A strip footing requires considerably more skill than a trench footing in its preparation. A formwork must be made to shape the concrete to the engineers design.

FBE 03 Building Construction Science Lecture 2 Foundations
Strip Foundation is one kind of foundation that transfers load from structures to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and settlement characteristics. It is possible to.
A strip foundation is a strip of concrete that runs beneath all load-bearing walls, as the name implies. The strip's width is determined by the soil's allowed bearing pressure and the building load. The strip must be long enough to rest on solid ground.
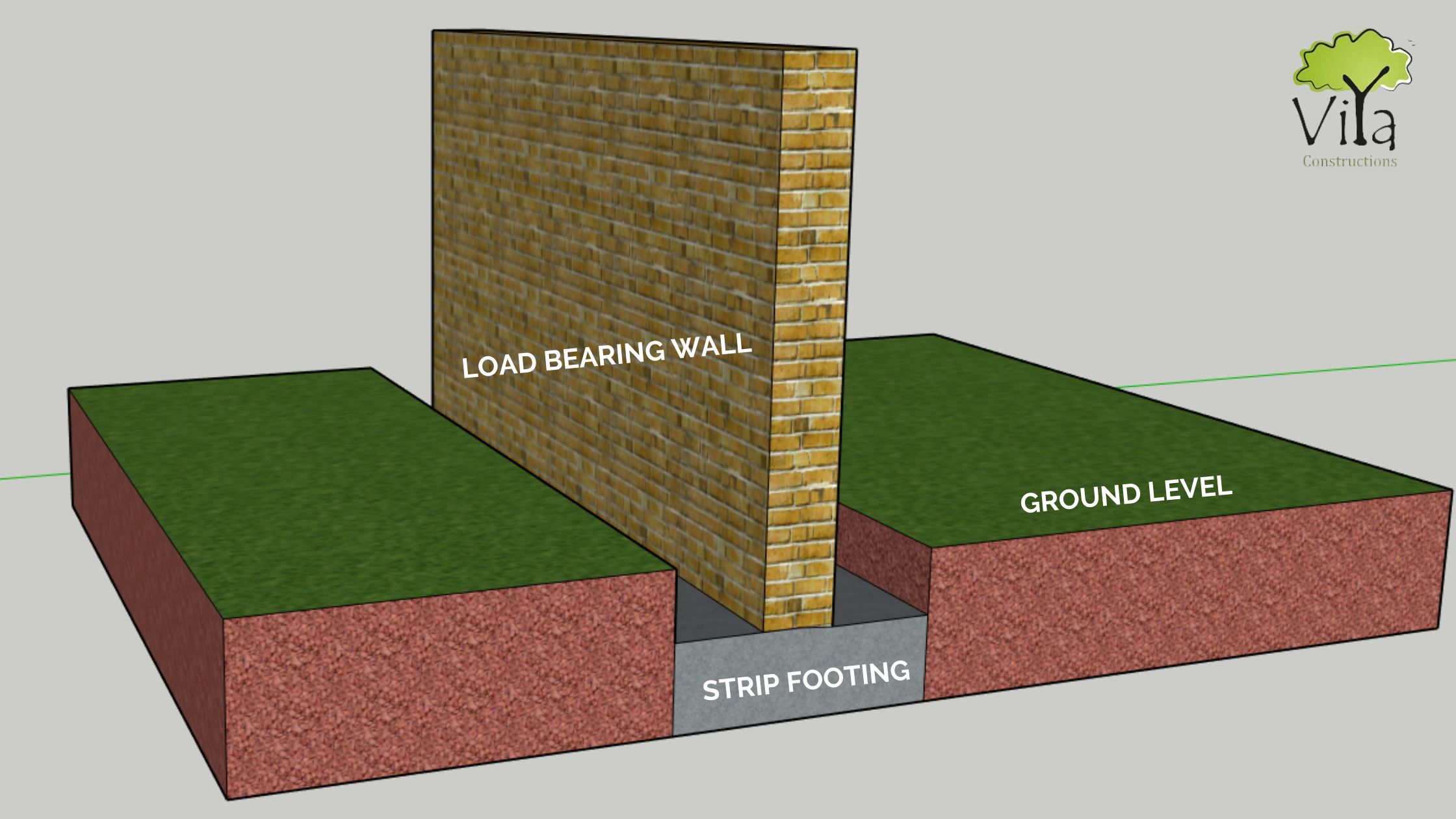
Strip Foundation or Strip Footing Viya Constructions
You can easily understand the types of foundation by following Sketch or Diagram. Types of Foundation With Sketches.. Strip Foundations consist of a continuous strip, mad e up of brick masonry/stone masonry/concrete formed centrally under load bearing walls. The continuous strip serves as a level base on which the wall is built and is of.
Building Guidelines Requirements for Foundations & Rising Walls
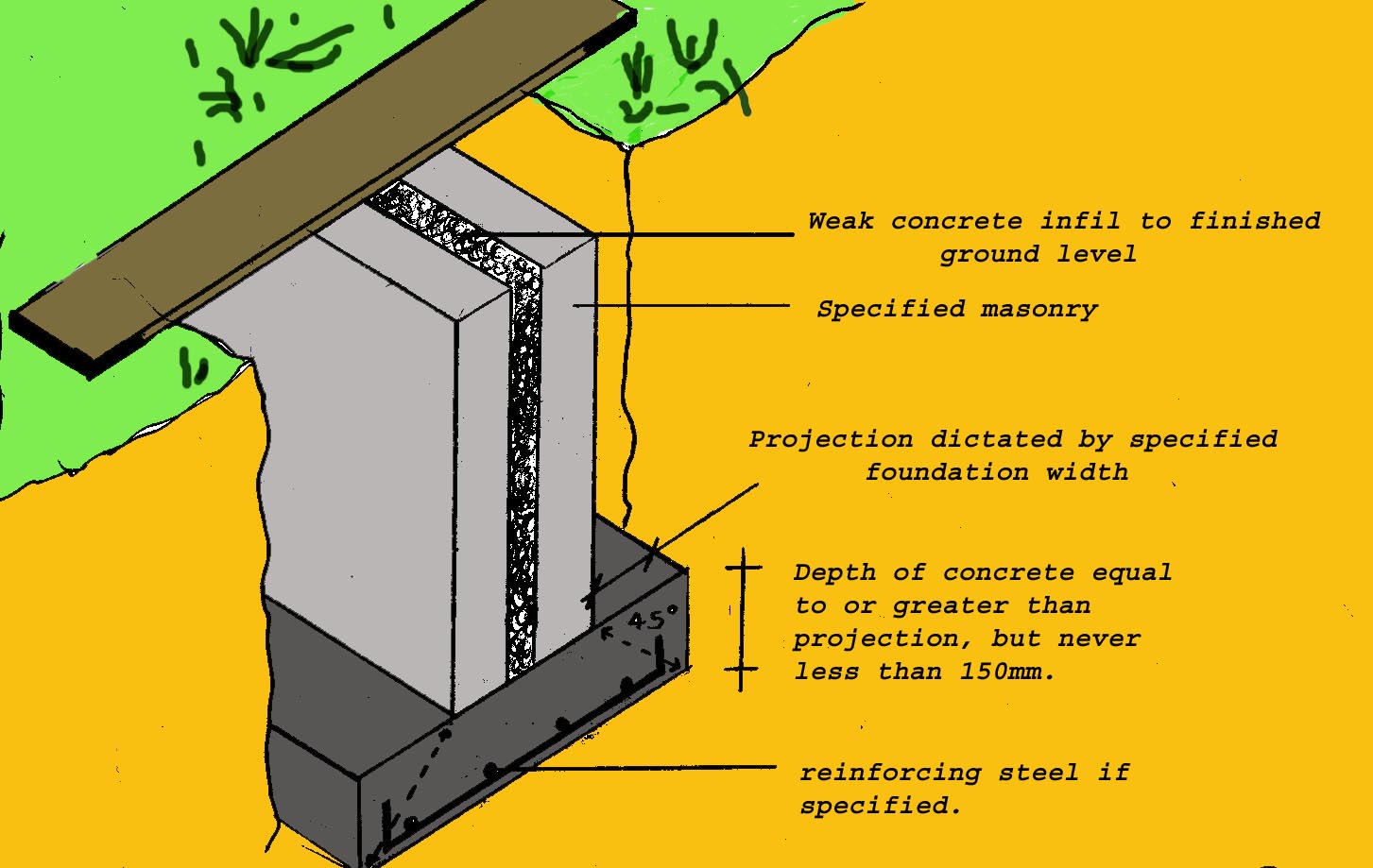
A strip foundation is quite simply a strip of concrete placed in a trench. The absolute minimum thickness of this strip is 150mm. Please note that all of the loading figures given here may not apply to your project and should be checked by an architect on site. Soil samples and tests may be necessary. When can I use a Strip Foundation?

Strip foundation Technobasalt
Types of foundation There are four main types of foundations: Strip foundation - the preferred and most common choice for low rise housing. Strip of concrete under all load bearing walls. Pile foundation- Long concrete members take the load of the building through weak soils to load bearing strata.. Pad foundation - More commonly used under point loads, such as columns, but can be used.

What do you mean by foundation in a building? Basic Civil Engineering
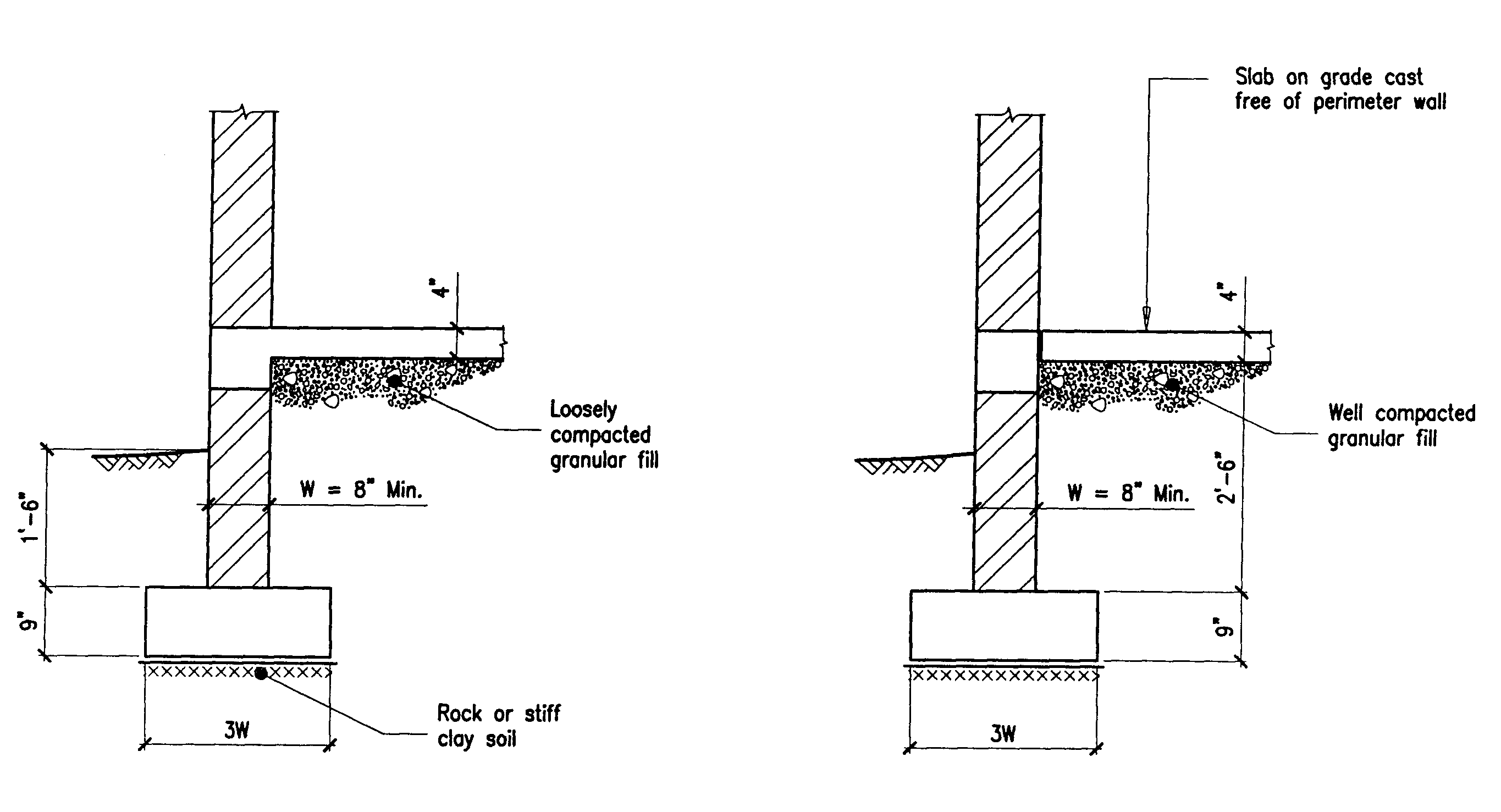
Strip Foundations. The thickness of a strip foundation should be between 150mm and 500mm. 300mm thickness is used in most small domestic works. Strip foundations are usually at least 600mm wide as this tends to be the width of the digger bucket although on sand, silt or soft clay, it may be necessary to provide foundations as wide as 850mm.
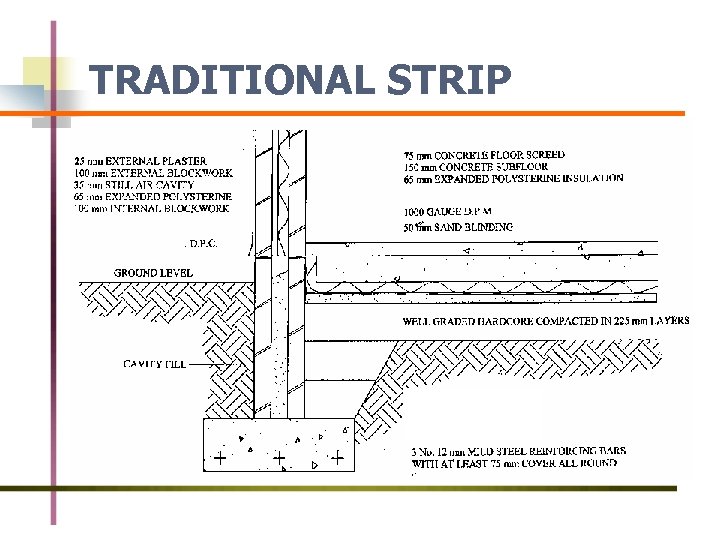
FOUNDATIONS FUNCTION OF A FOUNDATION n Safely
In the 'Strip Footings Results - Footing 3' dialog box that appears, you can check the values for axial load, moment as well as Shear, span moments and support moments used for the design.Click on the 'Diagrams' tab to see the loading, shear force and bending moment diagrams for the foundation as shown below.The results can also be printed using the buttons at the top right hand side.
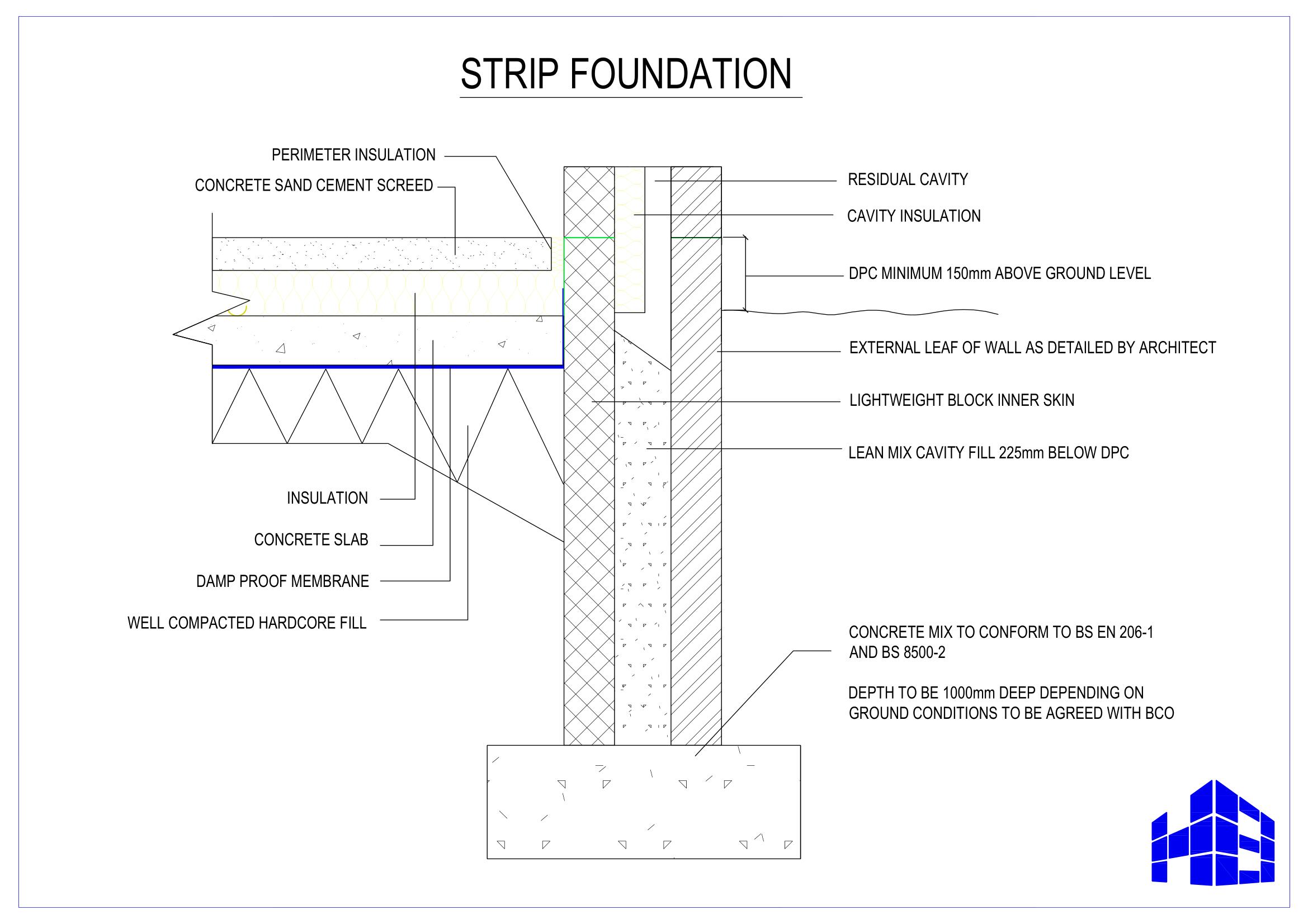
Building Guidelines Standard Construction Drawings Dwellings Strip Foundation
The principle design features of a strip foundation are based on the fact that the load is transmitted at 45 degrees from the base of the wall to the soil. The depth of a strip foundation must be equal to or greater than the overall width of the wall. The width of the foundation must be three times the width of the supported wall.